GCSE Science | Organic Chemistry

Crude oil
- crude oil can be burnt to produce energy but it is a finite resource
- crude oil is a mixture of short hydrocarbons and long hydrocarbons
- short hydrocarbons are more flammable, more runny, and more volatile
- long hydrocarbons are less flammable, more viscous, and less volatile
- longer hydrocarbons have stronger intermolecular forces
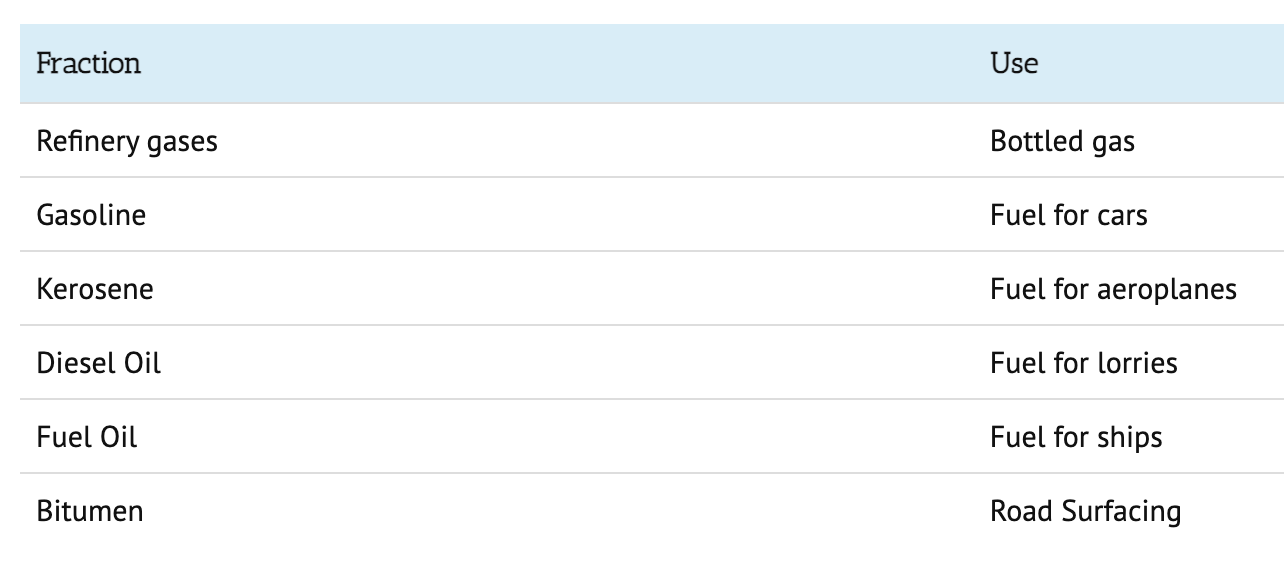
Fractional distillation
- fractional distillation is used to seperate the short, medium and long hydrocarbons
- vaporise the crude oil (heat) - so they turn into a steam/ vapour
- allow the vaporised crude oil to enter the column
- the column is hotter at the bottom and cooler at the top
- the long hydrocarbons have higher boiling points so they will condense quickly and leave the column
- the short hydrocarbons have lower boiling points so will rise more before they condense
Cracking
- long hydrocarbons produced from fractional distillation are not as useful as short hydrocarbons
- cracking breaks long chain hydrocarbons into short chain hydrocarbons
- conditions: high temperature (600o C), aluminium oxide catalyst
Homologous series
- each member has the same functional group and the same general formula
- consecutive members differ by CH2
Alkanes
- The general formula of alkanes is CnH2n+2
- Monkeys eat peanut butter can be used to remember the names of the first four alkanes - methane ethane propane butane
- alkanes are an example of a homologous series
- each member of a homologous series shares the same functional group
- each member of a homologous series has the same general formula
- each consecutive member of a homologous series differs by an extra CH2
Complete combustion
- excess O2
- Hydrocarbon + O2 --> CO2 + H2O
Incomplete combustion
- not enough O2
- Hydrocarbon + O2 --> CO + H2O
- Carbon monoxide (CO) is poisonous. It binds to the haemoglobin preventing the blood from carrying oxygen.
(Halogen) addition of alkenes
(Hydrogen) addition of alkenes
Polymers
- a long chain molecule made up of many monomers
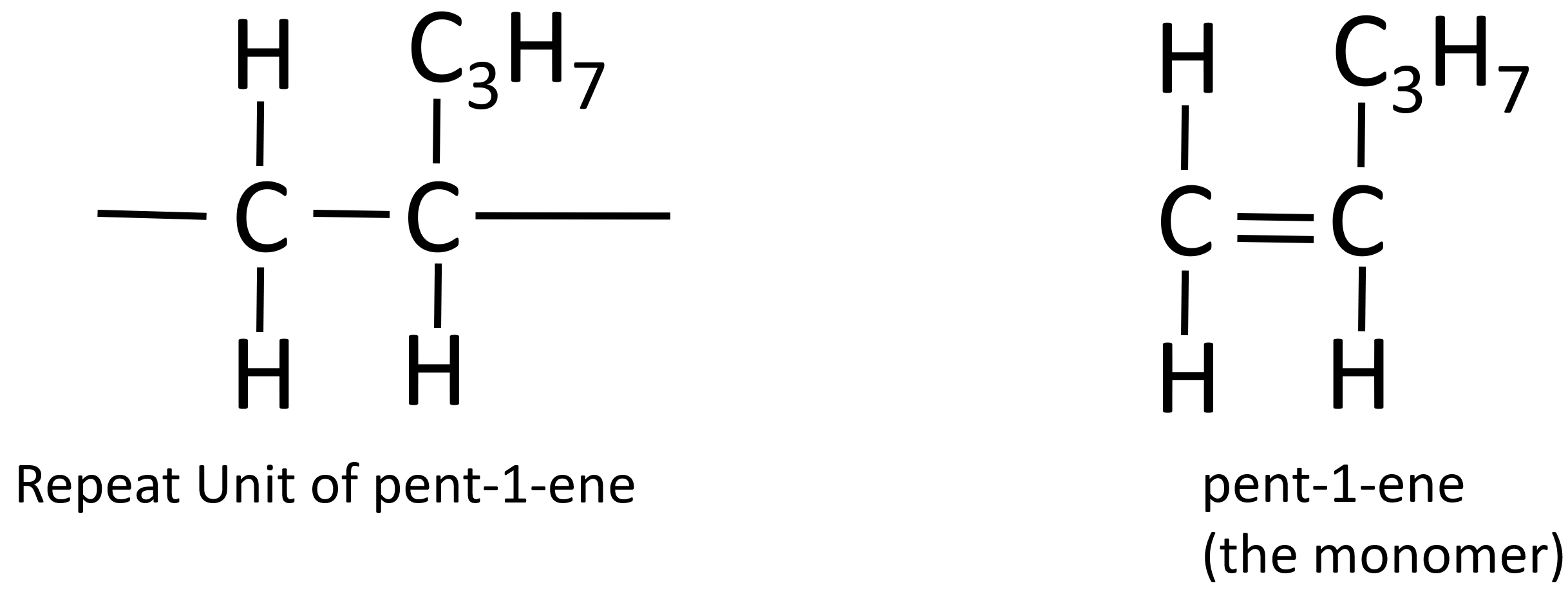
Addition polymerisation
- alkene monomers
- double bond breaks and opens up
- each monomer joins together
Oxidiation of alcohols
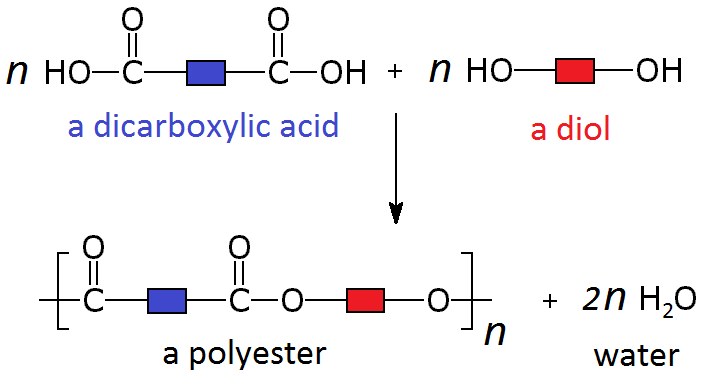
Condensation polymerisation
- di-ol and di-carboxylic acid monomers
- H2O is removed from the pair of monomers
- each monomer joins together