GCSE Science | Equilibrium
Last updated on
Dynamic equilibrium
- this is when the rate of forward reaction = rate of backward reaction
- concentration of reactants and products stay the same
- in a reversible reaction (⇌)
- in a closed system
- no substances are either added or escape from the system
Le Chatelier's Principle
- if the conditions of a dynamic equilibrium are changed, the equilibrium will move to counteract the change
- changes in temperature
- changes in concentration of the reactants
- changes in concentration of the products
- changes in pressure
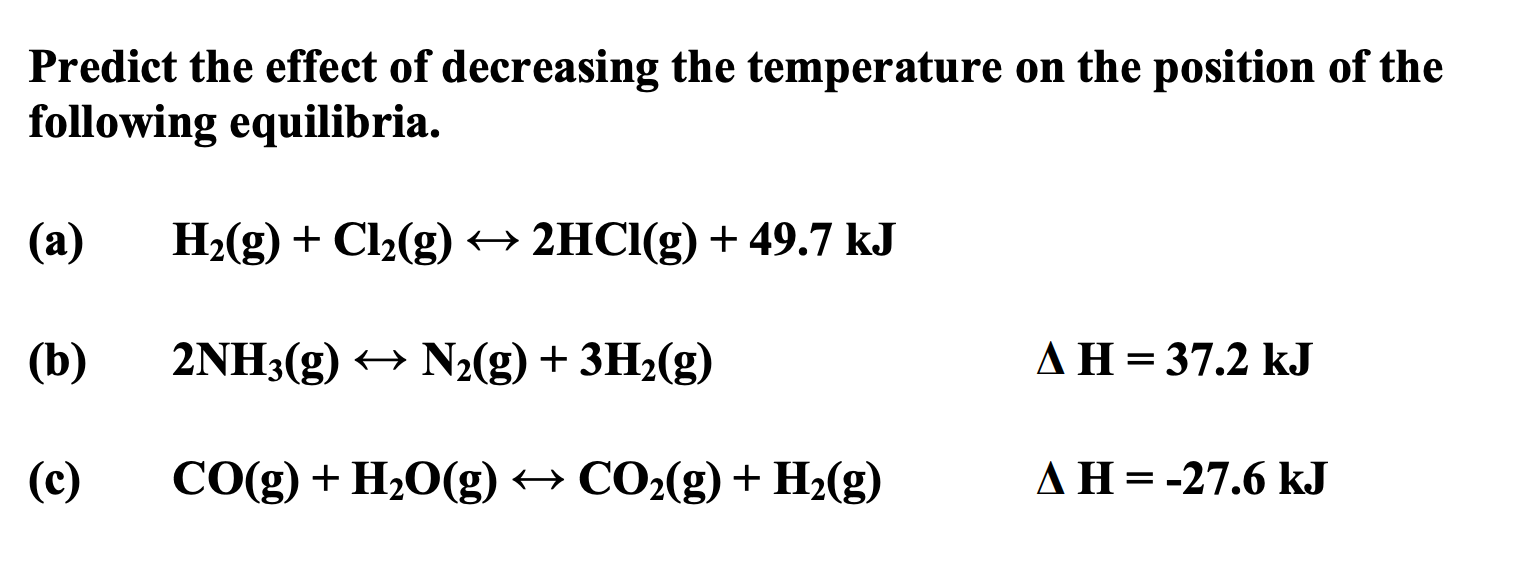
Examples - which way does equilibrium move?
- an increase in temperature - endothermic direction
- a decrease in temperature - exothermic direction
- an increase in pressure - side with fewer molecules of gas
- a decrease in pressure - side with more molecules of gas
- an increase in concentration of reactants - right
- a decrease in concentration of reactants - left
- an increase in concentration of products - left
- a decrease in concentration of products - right
Question 1

Question 2

Question 3

Question 4
Triple Science Only
Haber process
- N2(g)+3H2(g)⇌2NH3(g)
- (The forward reaction is exothermic)
- The process/ reaction used to produce ammonia
- Rate of reaction - we want this to be fast
- high pressure
- high concentration
- high temperature
- Equilibrium - we want this to be shifted towards the right
- high temperature - to shift equilibrium in exothermic direction
- high pressure - to shift to side with fewer moles of gas
- Overall compromise
- high pressure - although expensive - 200 atm
- temperature - 450o C - a compromise between faster rate and higher yield
- iron catalyst
- 2SO2(g) + O2(g) ⇌ 2SO3(g)
- (The forward reaction is exothermic)
- Rate of reaction - we want this to be fast
- high pressure
- high concentration
- high temperature
- Equilibrium - we want this to be shifted towards the right
- high temperature - to shift equilibrium in exothermic direction
- high pressure - to shift to side with fewer moles of gas
- Overall compromise
- pressure - 2 atm - a higher pressure isn't needed as yield is already high. cheaper to use a low pressure.
- temperature - 450o C - a compromise between faster rate and higher yield
- vanadium oxide catalyst



