GCSE Science | Electricity
Last updated on
Circuit symbols
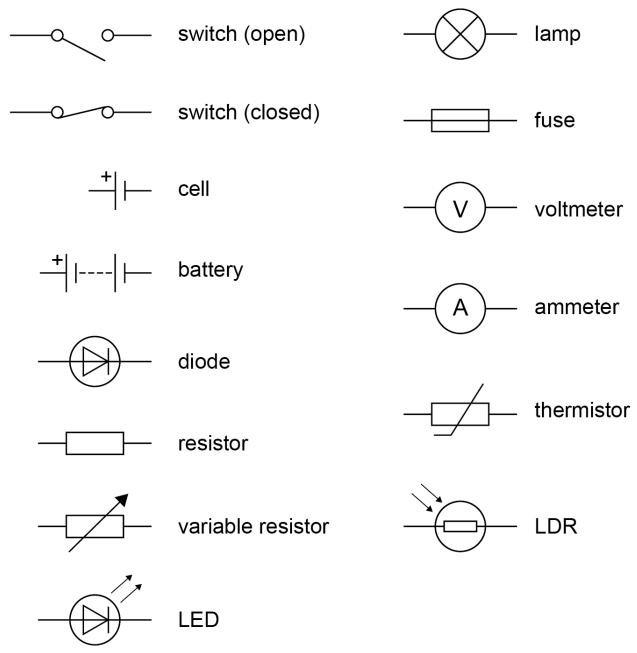
- Cells: has a potential difference - this pushes charge (electrons) around the circuit
- Batteries: two or more cells
- Open switch: off
- Closed switch: on
- Ammeter: measures current (connect in series).
- Voltmeter: measures potential difference (connect in parallel).
- Fixed resistor: controls current
- Variable resistor: also controls current - allows you to change the current
- Diode: prevents current from flowing in reverse
- Thermistor: temperature dependent resistor - as temperature increases, resistance decreases automatically (thermostats)
- LDR: light dependent resistor - as light intensity increases, resistance decreases automatically (street lamps)
Important equations
- Current: Q/t = current is the rate of flow of charge
- Q = It
- Q: charge (C), I: current (A), t: time (s)
- V = IR
- V: potential difference (V), I: current (A), R: resistance (Ω)
I-V graphs
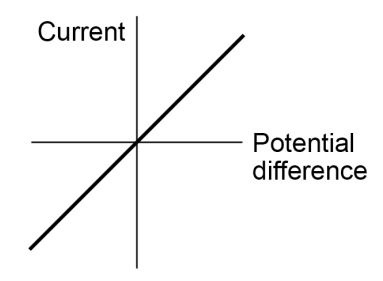 IV Graph for fixed resistor
IV Graph for fixed resistor- In a fixed resistor, the I-V graph is a straight line - this shows the resistance remains constant.
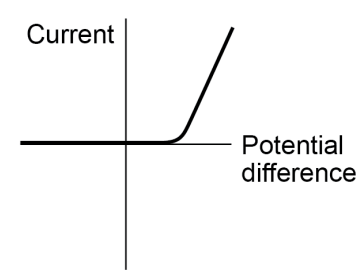 IV Graph for diode
IV Graph for diode- In a diode, the I-V graph does not go down - this shows that current cannot flow backwards.
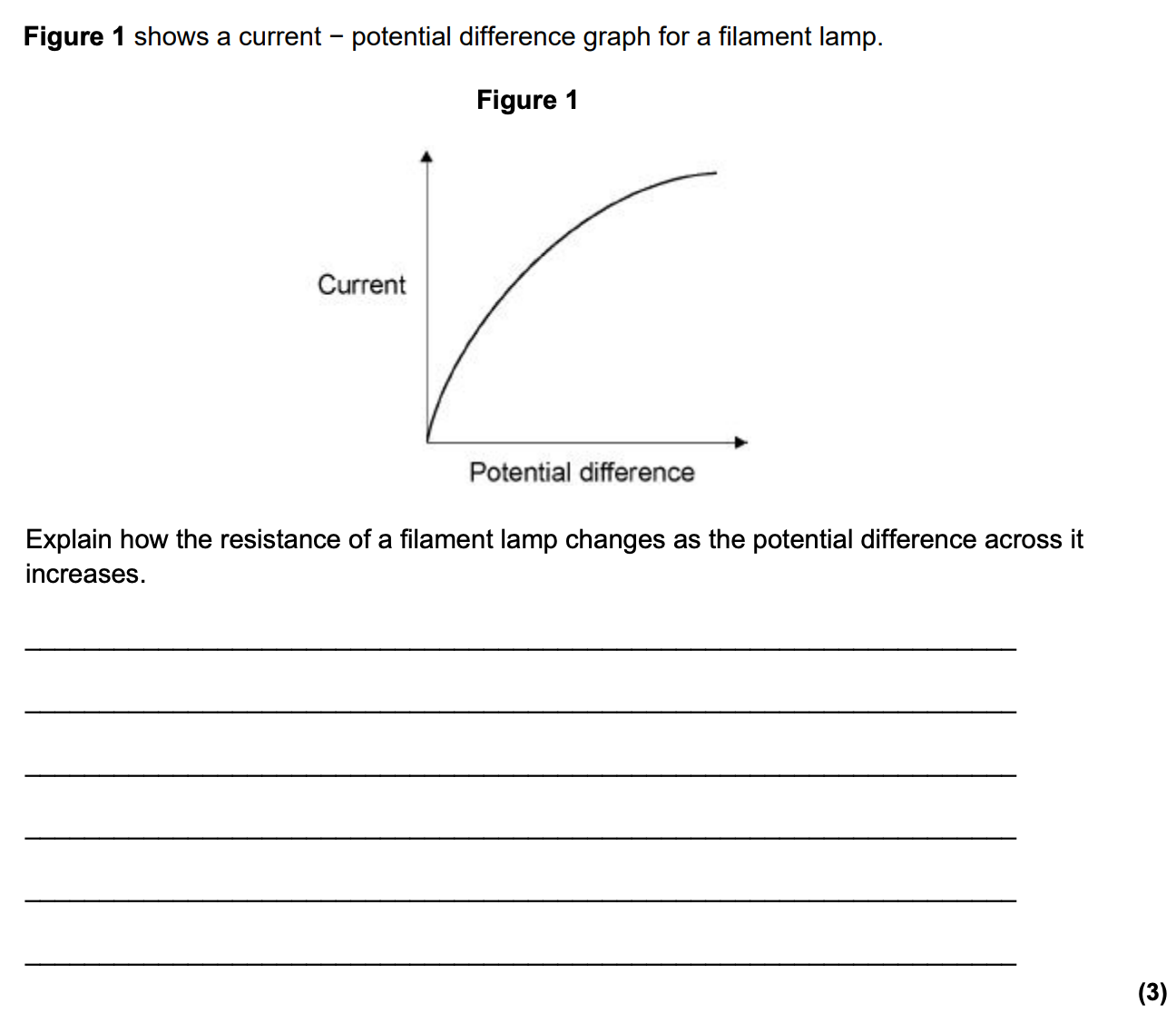
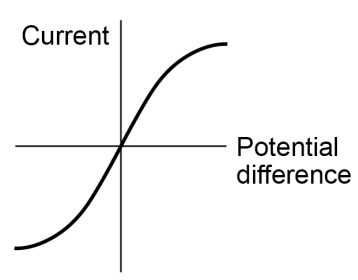 IV Graph for filament lamp
IV Graph for filament lamp- In a filament lamp, as potential difference increases,
- current increases
- temperature increases
- resistance increases
- current stops increasing
Question 1
Series circuits
- current is the same everywhere
- p.d of each component adds up the p.d. of the cell or battery
- resistance of each resistor adds up to the total resistance of the circuit
- ratios of resistance in each component is the same as the ratio of p.ds
Question 2
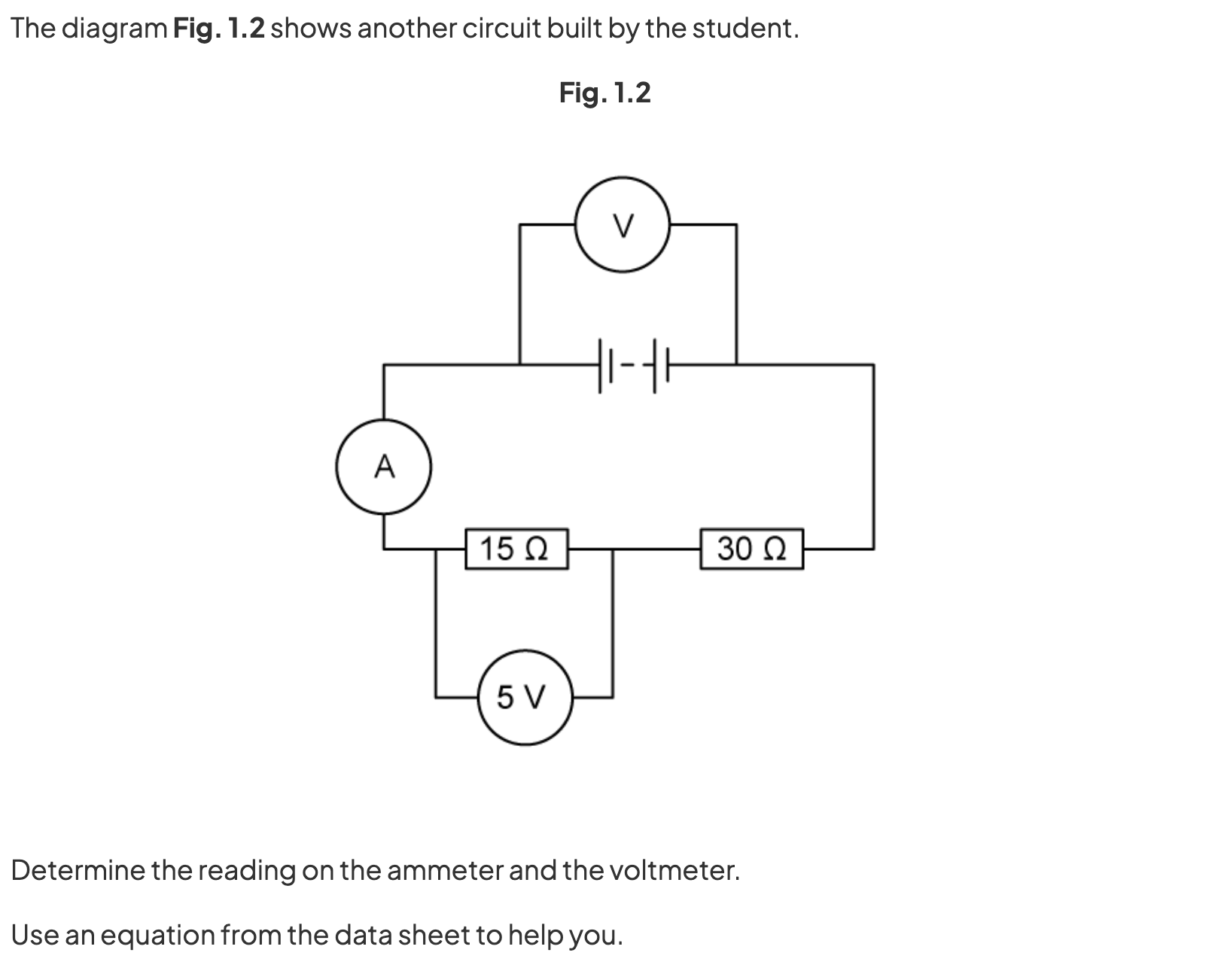
Question 3
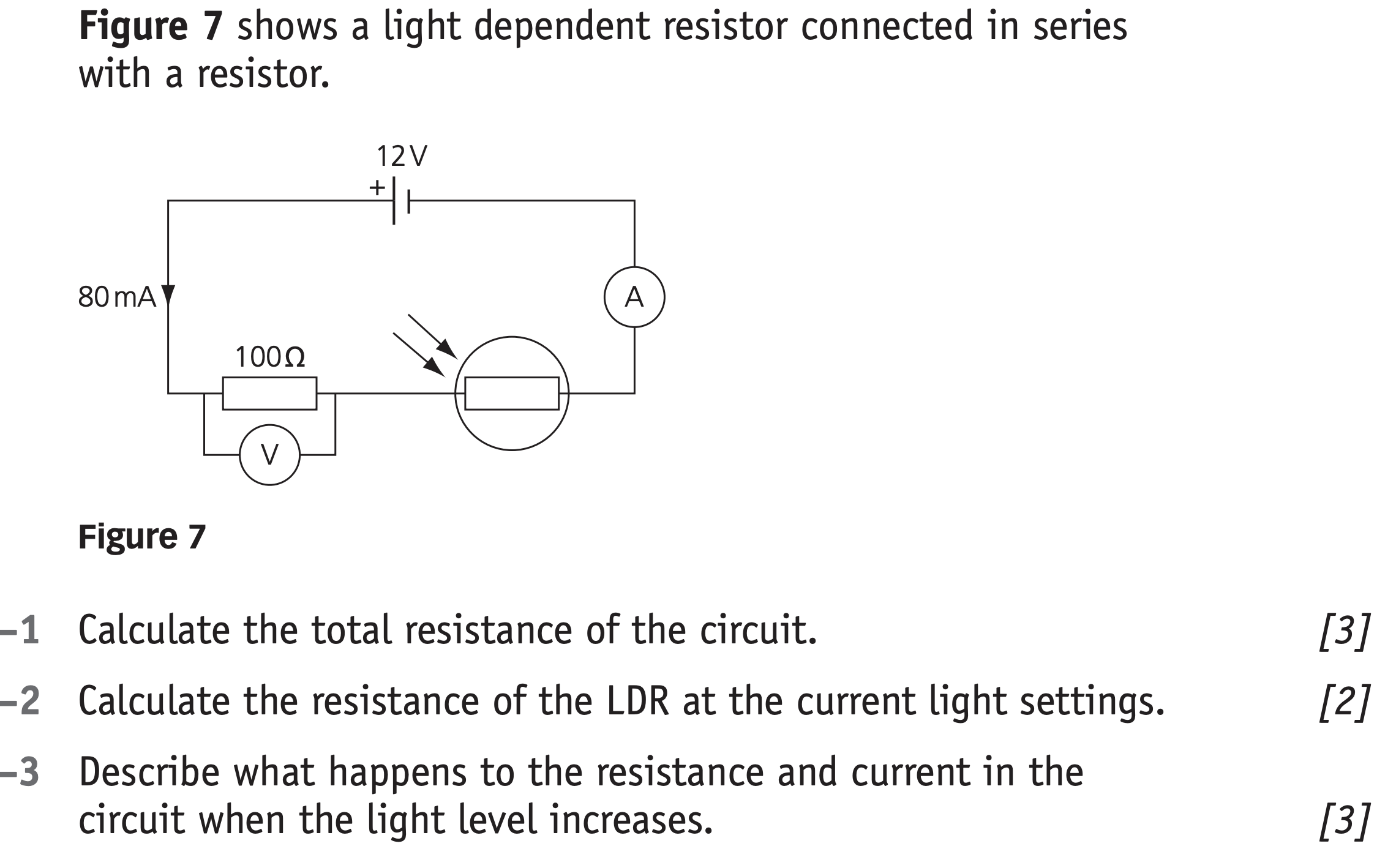
Question 4
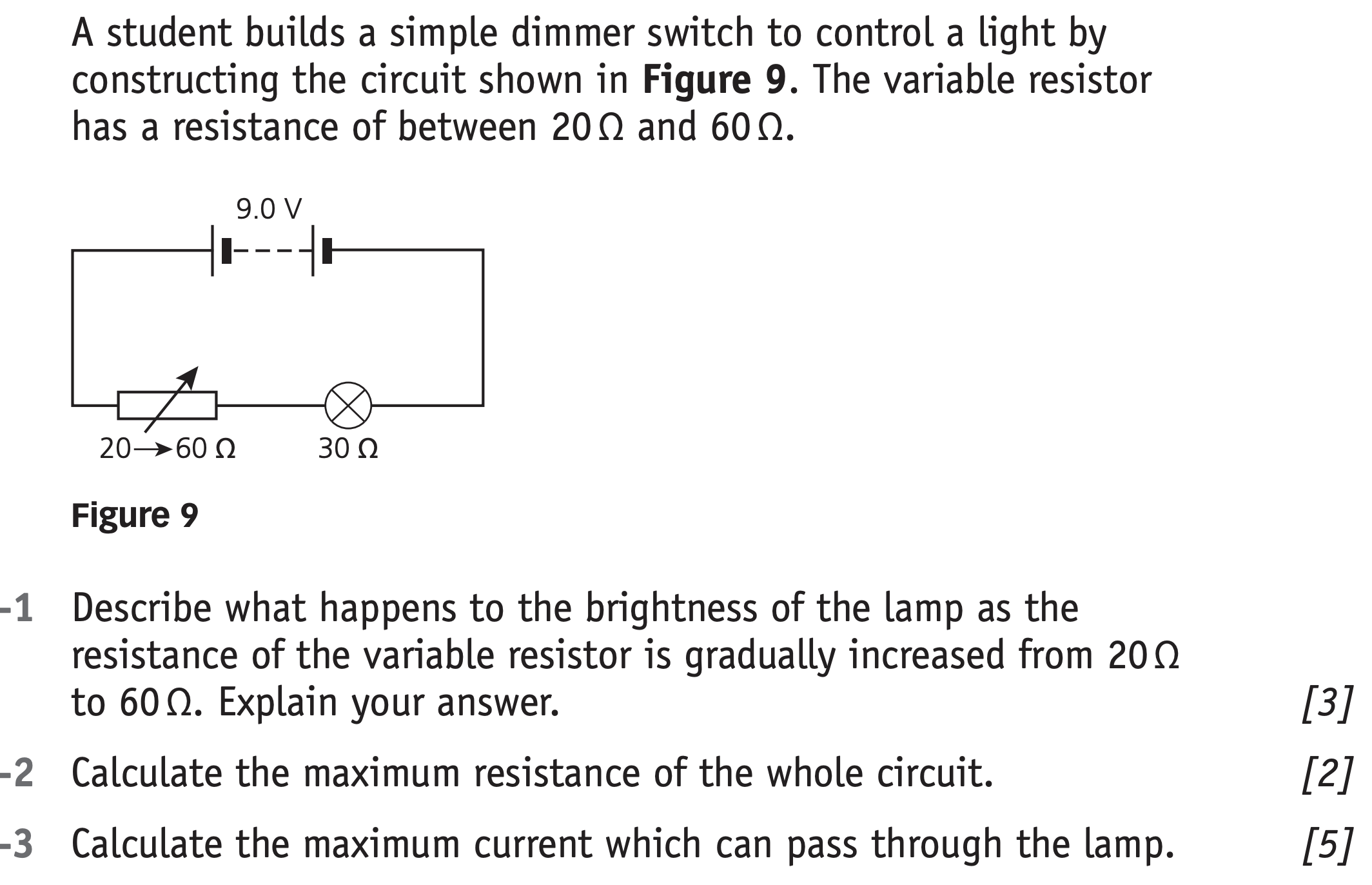
Parallel circuits
- current from each branch adds up
- p.d. is the same everywhere
- adding more resistors decreases the circuit's total resistance as there would be more branches for the current to flow through
Question 6
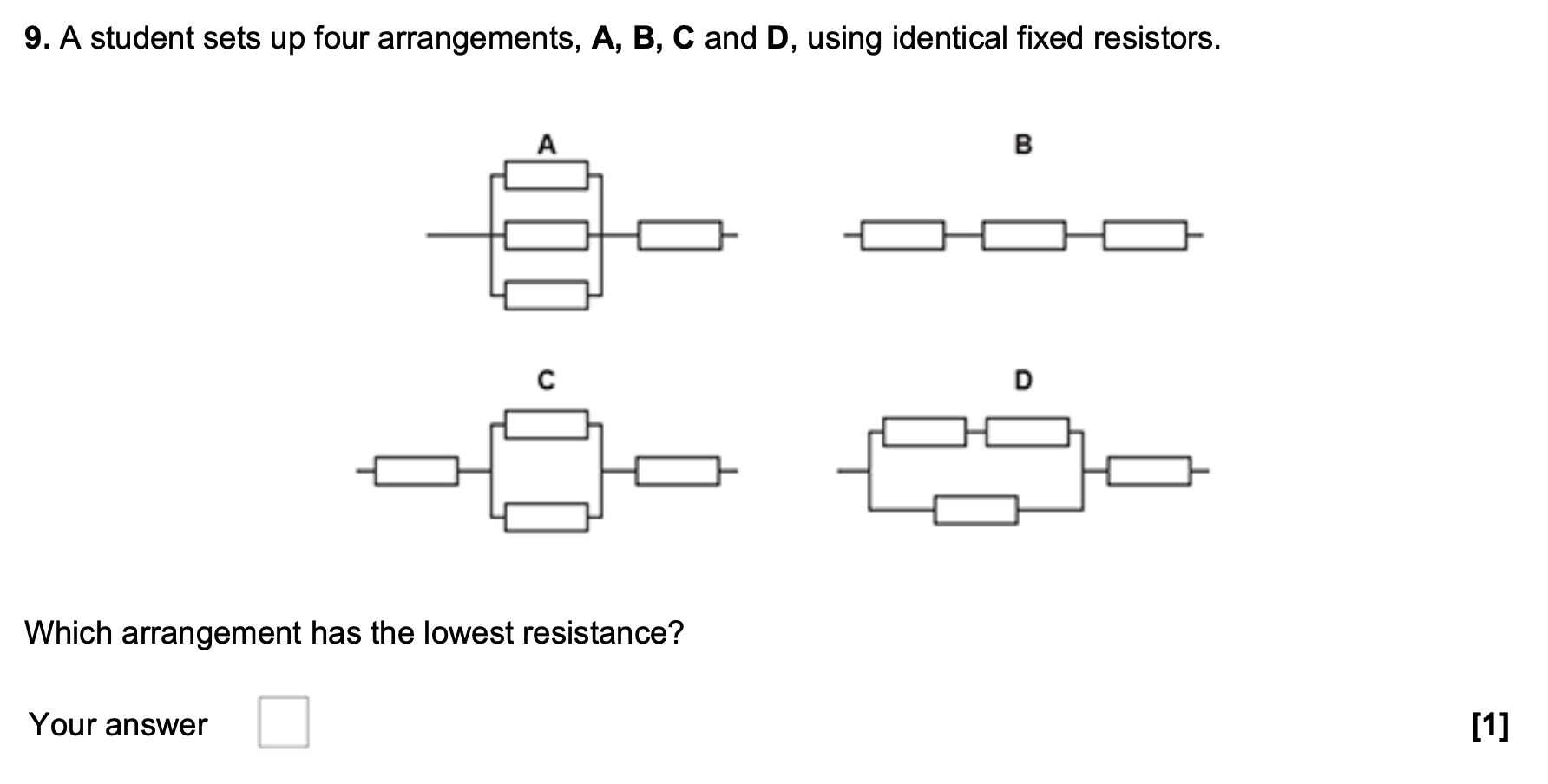
Question 7
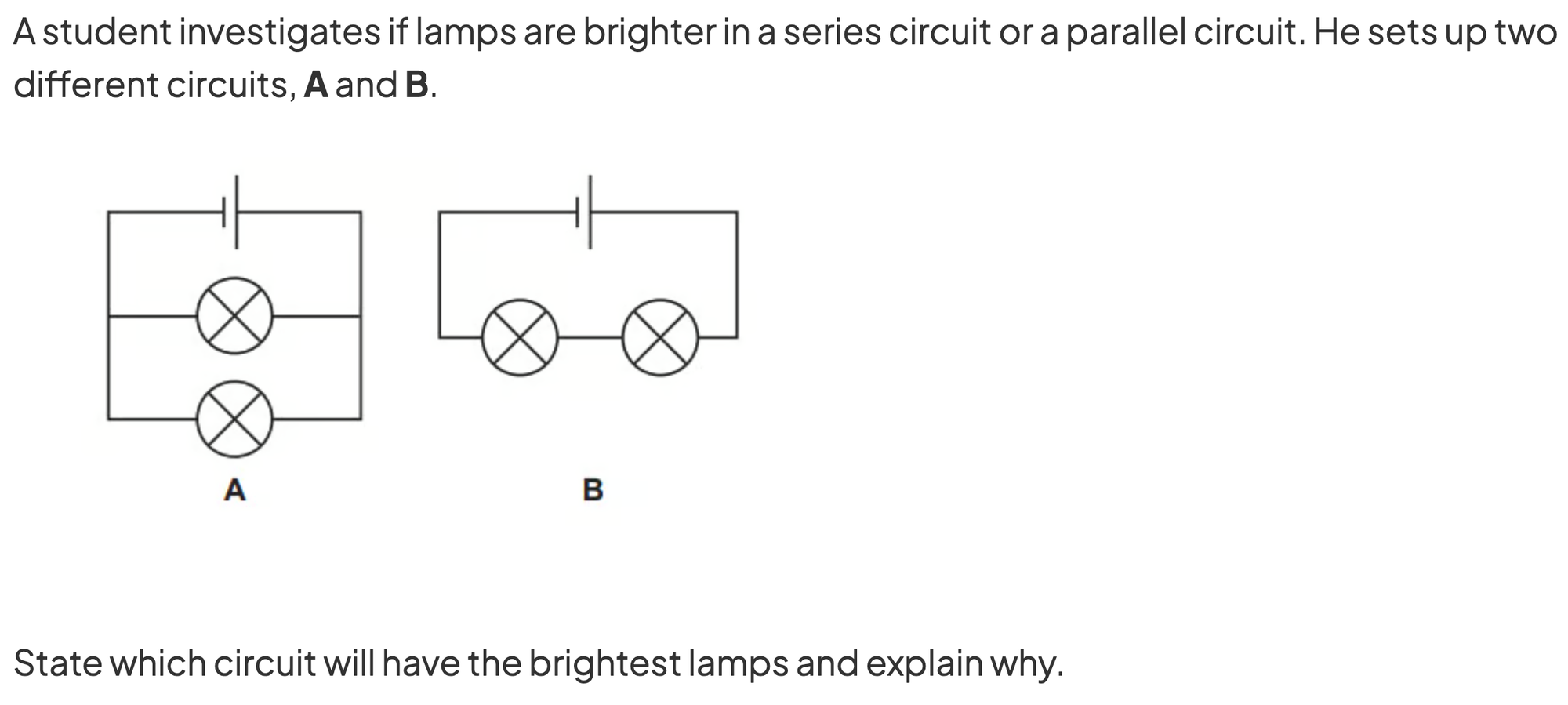
Question 8
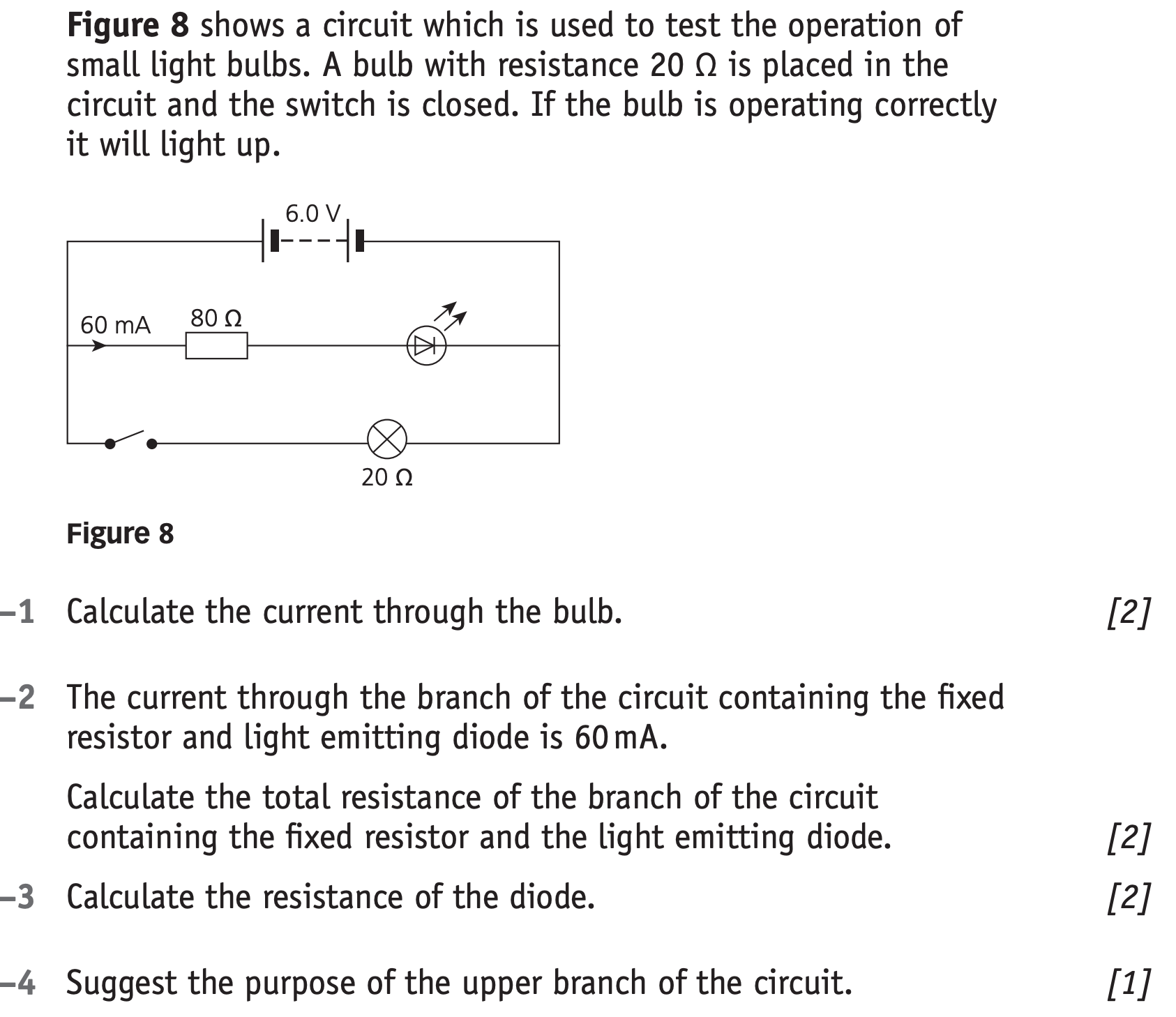
Question 9
- the ratio of resistance between components is the same as the ratio of the potential difference between components
- e.g. if resistance is 2000: 1000 then potential difference also has the ratio 2: 1
Question 10
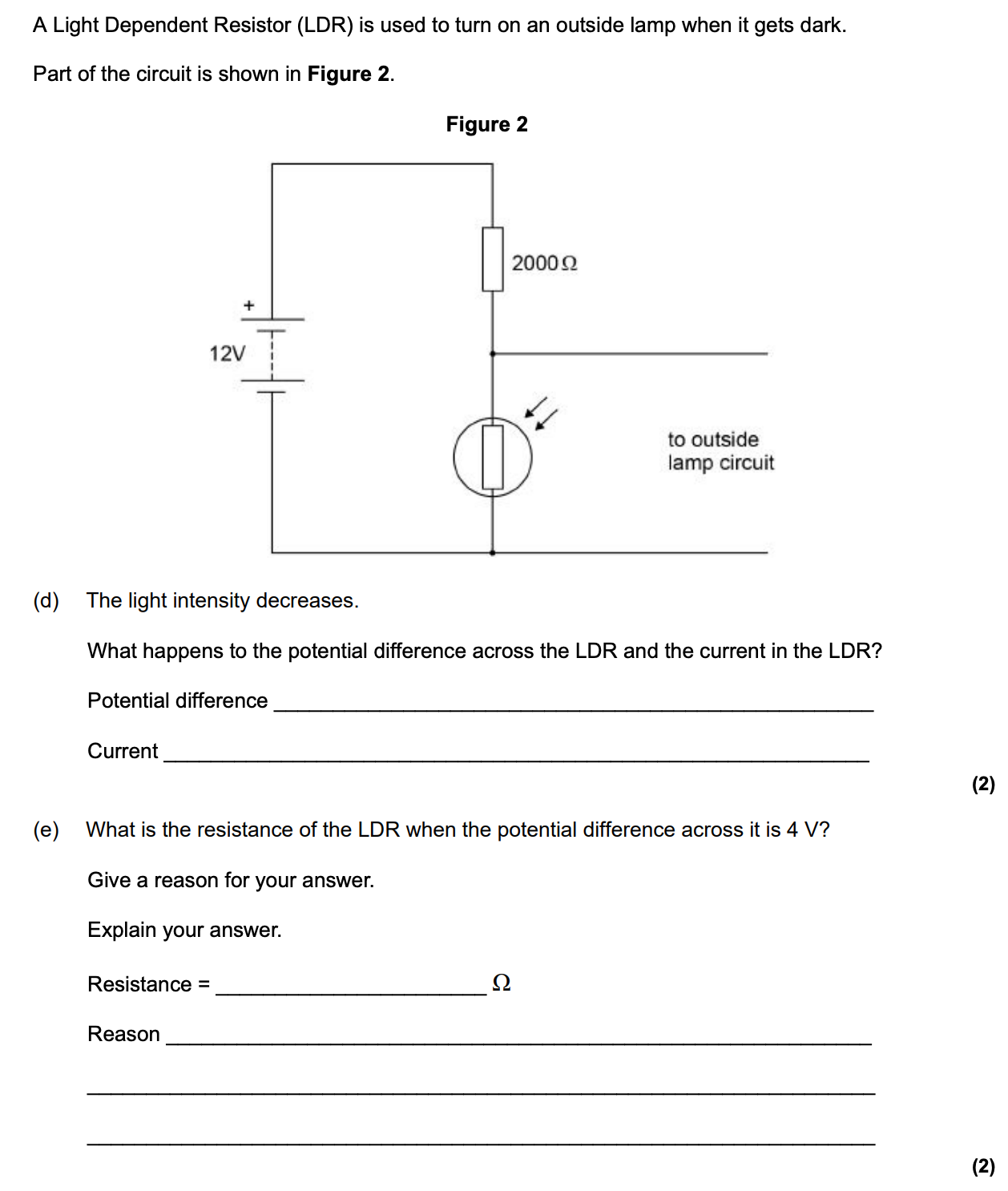

Question 11

Question 12
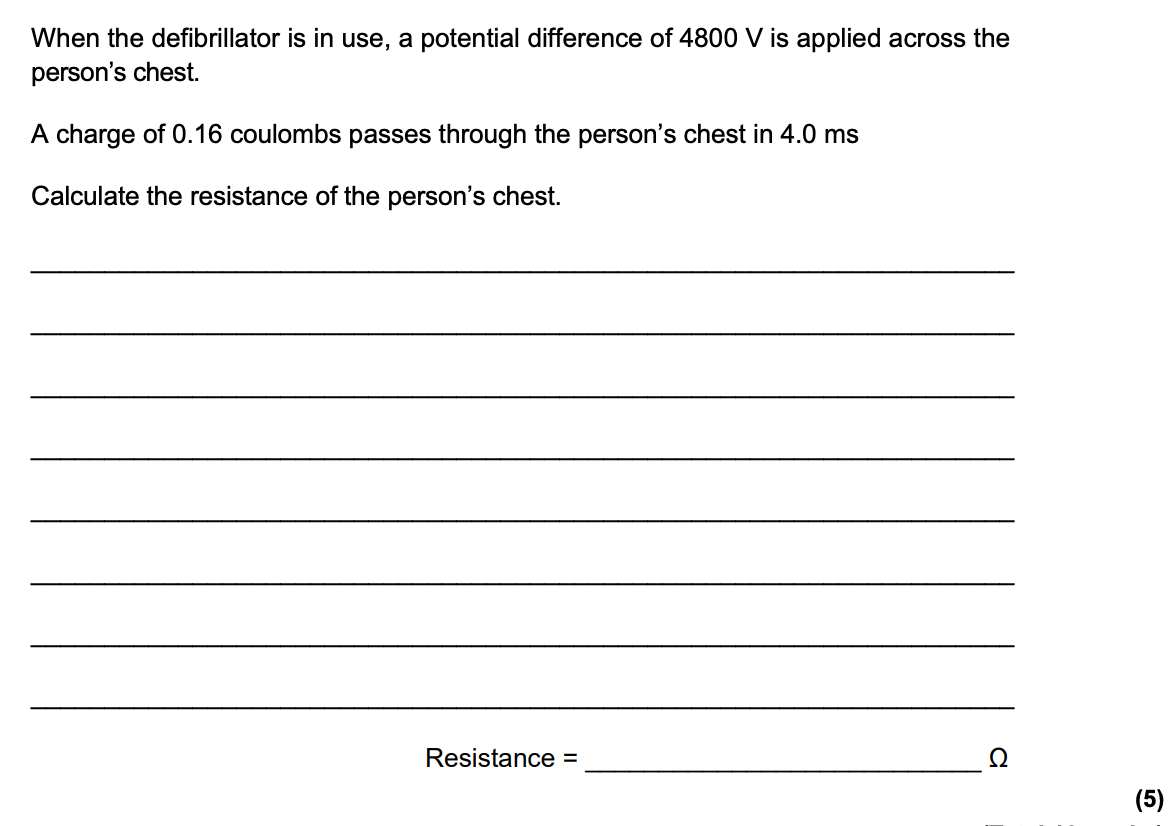
Question 13

Question 14

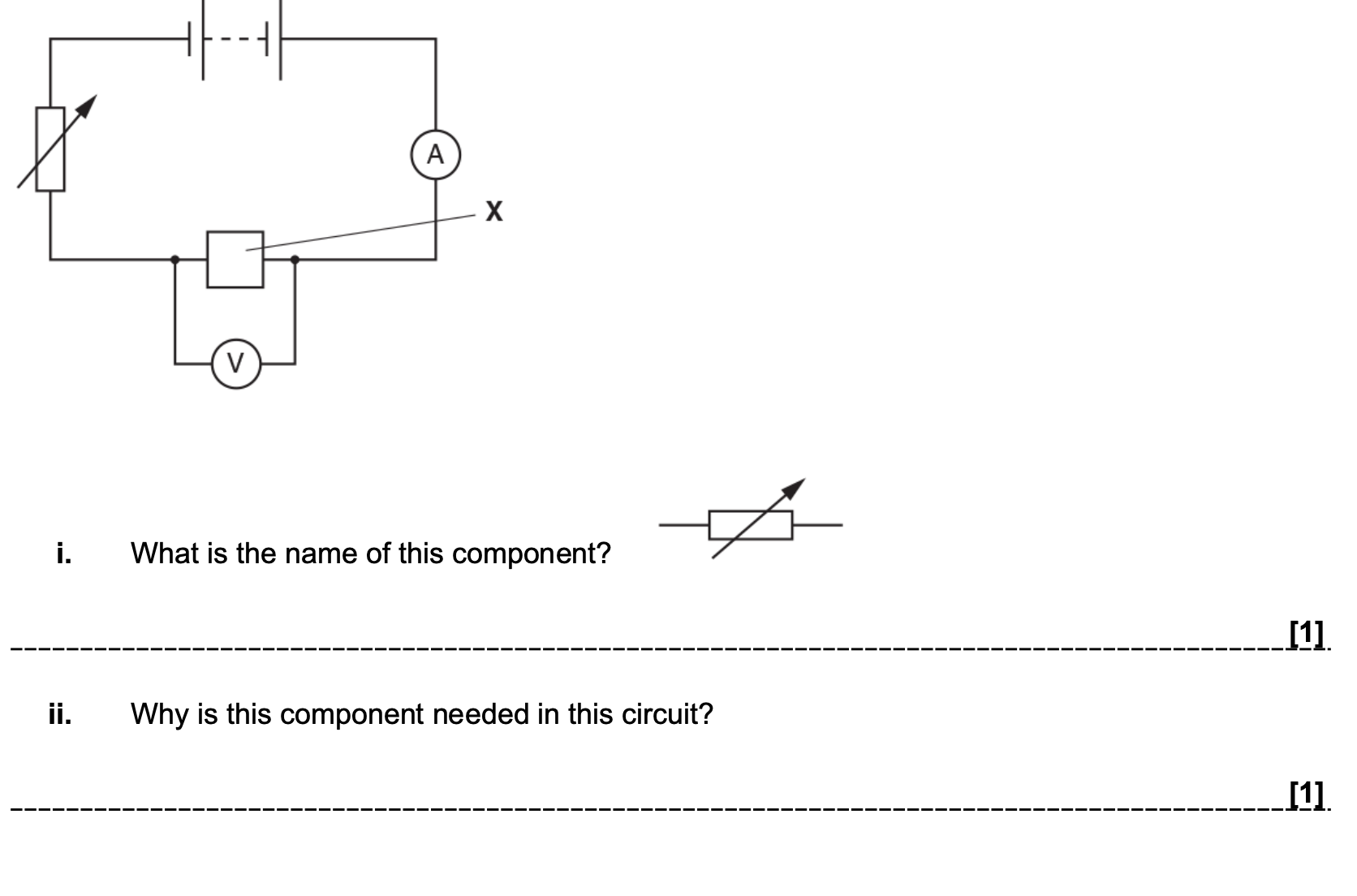
Practical - investigate the I-V characteristics of a fixed resistor
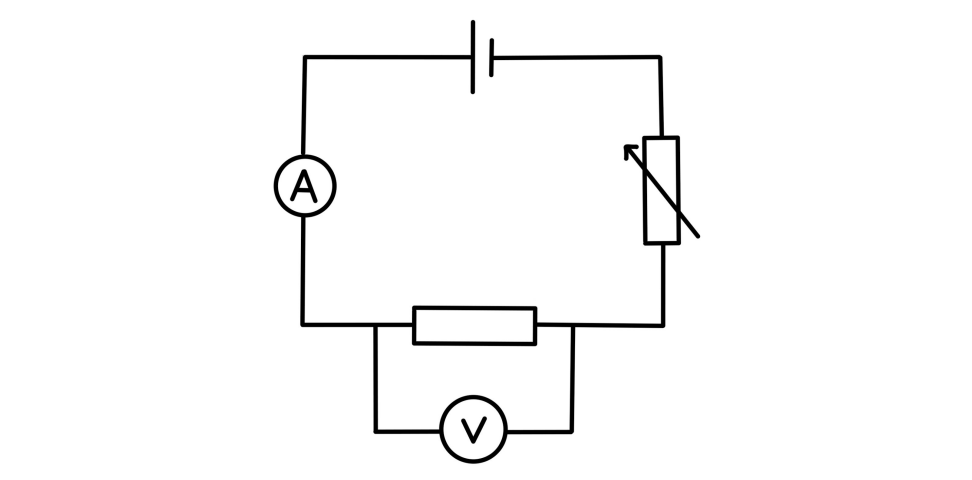
- set up the circuit as shown
- record the current by using the ammeter
- record the potential difference by using the voltmeter
- adjust the setting of the variable resistor - this will vary the resistance, and therefore it will also vary the current
- then repeat steps 2 and 3
- plot a graph of current against potential difference
Wires
- live wire - 230 v - carries the p.d
- earth wire - 0 V - safety circuit
- neutral wire - 0 V - connects the circuit


















