GCSE Science | Acids and Bases
Last updated on
What do all acids contain and what is their pH?
- H+ ions
- pH is closer to 1 for strong acids and closer to 6 for weak acids
What are the common ions?
- nitrate - NO3-
- sulfate - SO42-
- carbonate - CO32-
- phosphate - PO43-
What are the common acids?
What is the difference between a strong acid and a weak acid?
- strong acids completely disocciate in water
- weak acids partially disocciate in water
What happens to [H+] if pH goes up by 1?
- concentration of H+ ions
- goes down
- by 1/10th
What happens to [H+] if pH goes down by 1?
- concentration of H+ ions
- goes up
- by x10
What is a salt?
- A salt is formed when
- the H+ ion in the acid is replaced by a metal ion
Acid and base reactions
- acid + metal --> salt + hydrogen
- acid + metal oxide --> salt + water
- acid + metal hydroxide --> salt + water
- acid + metal carbonate --> salt + water + carbon dioxide
Ionic equation for neutralisation
Titrations
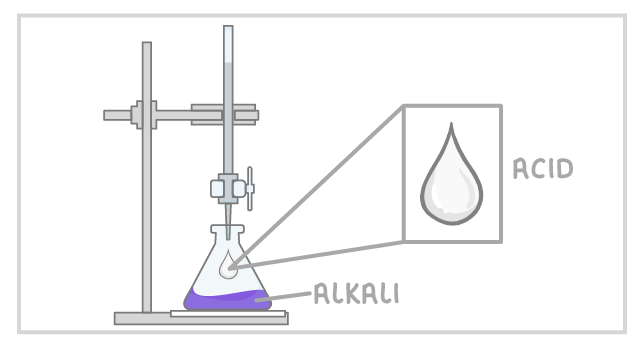
- used to figure out the concentration of a known acid
- fill the conical flask with the acid with an unknown concetration
- fill the burette with an alkali with a known concentration
- add indicator (colour will change as the acid is neutralised)
- let the alkali drop into acid until the colour changes (rough reading/ trial run)
- measure final volume - initial volume on burette
- repeat but slow down the tap to get the exact volume needed
- repeat three times
- only use concordant results (between 0.1cm3 of each other)
- conduct calculations to work out the concentration
