Explain ways in which a government can use fiscal policy to affect the pattern of economic activity
Extract F (lines 1–2 and 8) states: ‘As part of fiscal policy, government spending can be used to allocate resources to different regions and sectors of the economy and consequently, change the pattern of economic activity...Taxation also has a role to play in affecting the pattern of activity’.
Explain ways in which a government can use fiscal policy to affect the pattern of economic activity. (June 2022)
Fiscal policy is the use of government spending and taxation to influence the level of aggregate demand in the economy. Aggregate demand is the total planned spending in the UK economy.
Expansionary fiscal policy is when there is an increase in government spending or a decrease in taxation, which leads to a right shift in the aggregate demand curve. This is because AD = C + I + G + (X-M), and there is an increase in G.
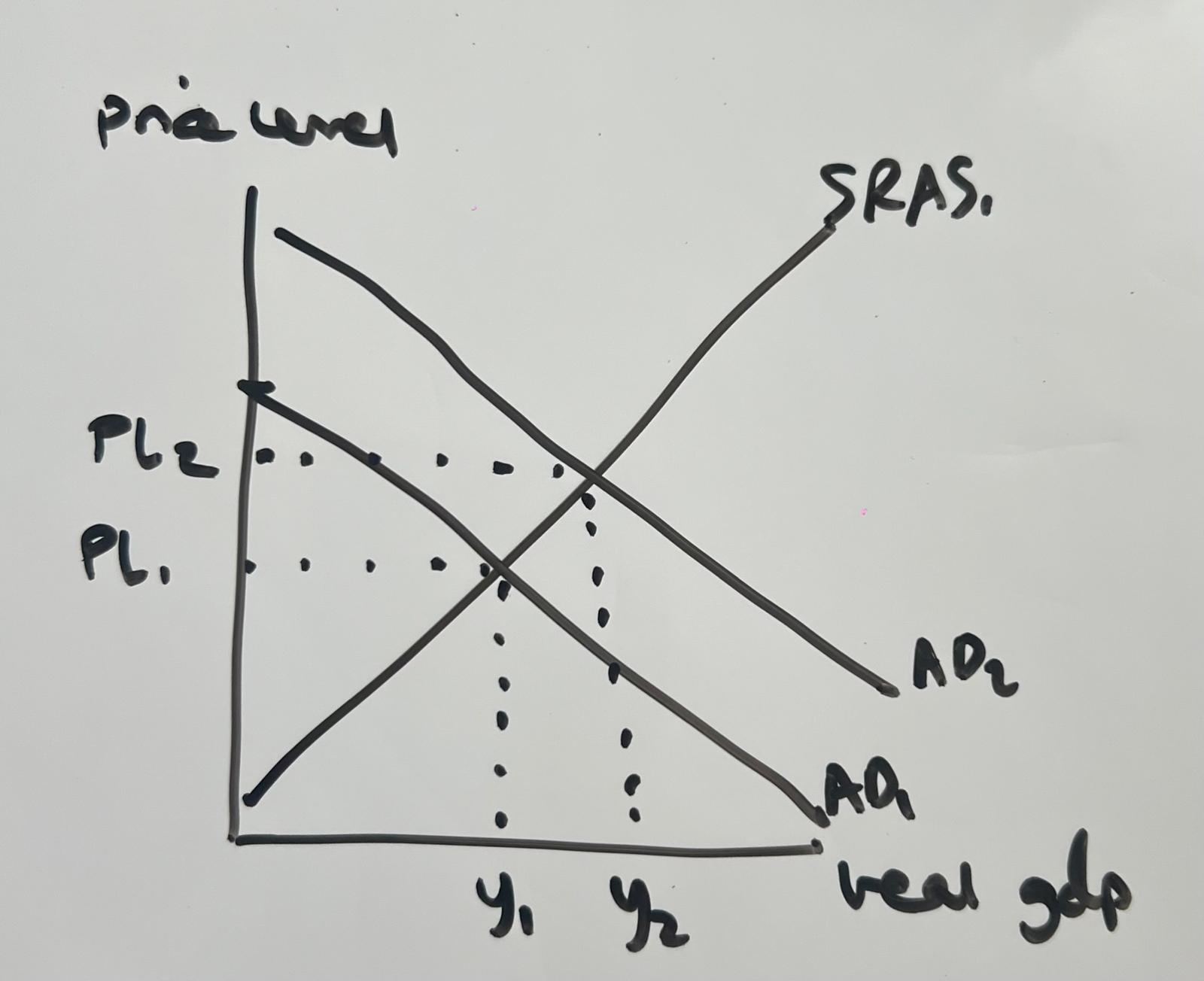
The diagram shows that the right shift in AD causes an increase in real GDP (economic growth) from y1 to y2, which should also lead to a decrease in unemployment as there is a greater demand for workers due to the greater demand for goods and services. There is also an increase in the price level from PL1 to PL2, which is known as inflation. This is because there is more demand chasing the same number of goods and services.
Paragraph 2 example
- Contractionary fiscal policy
- Decrease in government spending or an increase in taxation
- AD = C+I+G+(X-M)
- Left shift in AD
- Decrease in price level (disinflation) back towards the target
- Less demand chasing the same number of goods and services
- Decrease in real GDP
- Increase in unemployment
- Less derived demand for labour due to less demand for goods and services
- Lower disposable incomes
- Less consumer confidence and less consumer spending
- Further left shift in AD
- Negative multiplier effect