Edexcel AS-Level Economics Paper 1 June 2023 | Model Answers
This page contains a model answer to Section B from the Edexcel AS-Level Ecoomics Paper 1 from June 2023.
Edexcel AS-Level Economics Paper 1 June 2023
With reference to Figure 1 and Extract A, explain the relationship between price elasticity of demand and total revenue. (5 marks)
If a firm is selling a good that is inelastic in demand, they can increase their prices and their total revenue will increase. Total revenue is price x quantity. Price elasticity of demand is the percentage change in demand divided by percentage change in price. Figure 1 shows that the PED for streaming services is -0.6 meaning that they are inelastic. Firms like Netflix are able to raise their prices and will see an increase in total revenue.
With reference to Extract B, explain two external benefits associated with the consumption of ‘public service broadcasting’ (line 2). (6 marks)
An external benefit is a positive impact on a third party from a transaction. A third party is someone other than the buyer or the seller. For example, if someone learns something new from the news or from a documentary, they can share this knowledge to other people. So, someone other than the consumer is also benefiting from the consumption of public service broadcasting. Extract B, Line 12 says that the BBC's Charter aims 'to support learning for people of all ages'.
Another example is that when children watch TV, they may improve their English speaking skills, and this will benefit them at school. Their parents or school teachers will feel some benefit from this too. Another mission of the Charter was 'to reflect the UK, its culture and values to the world' (Line 16).
‘Television content is a public good’ (Extract B). Assess this statement. (10 marks)
Some may argue that TV content is a public good. A public good is non excludable and non rival. TV is non rival meaning that if one person watches TV, this does not reduce the ability for anyone else to watch TV. In theory, infinite people can watch the same TV channel at the same time. Public goods are also non excludable. This means it is impossible to prevent anyone from accessing the service. If something is non-excludable, it leads to the free rider problem. Extract B says 'very few people would pay due to the free rider problem.' If the TV channel is already running, there is no reason for anyone to pay.
However, you could argue that TV is excludable. For example, there is an enforcable TV license fee which people have to pay in order to watch TV. BBC iPlayer asks users to confirm that they have a TV license when they sign in. There are also many TV channels and platforms which require subscriptions or fees to watch. Also, over time, technology enables the excludability of TV services to increase. For example, Netflix is now able to detect if people are sharing Netflix logins and prevent this from being outside of a family or household. Therefore some may argue that TV is a quasi public good.
Using examples from the information provided, explain what is meant by both ‘substitutes’ and ‘complementary goods’. (4 marks)
Cross elasticity of demand is the percentage change in demand of good A divided by the percentage change in price of good B. Complementary goods such as a TV and a TV remote would have a negative XED. On the other hand, substitute goods like Netflix and Amazon Prime Video subscriptions would have a positive XED. As Netflix subscriptions increase in price, the demand for Prime Video would increase.
Discuss likely reasons why the market price of streaming television content is increasing. Draw a supply and demand diagram to support your answer. (15 marks)
One reason the market price for streaming television content is increasing is because of greater costs of production. This causes supply to shift to the left. Supply is the number of goods and services that firms are willing and able to produce at each given price. So, if costs of production rise then firms are going to find it difficult to produce as many goods and services at each price point. Extract A Line 10 states that 'the costs of providing streaming television content have risen' and it also mentions that each episode of Stranger Things costs £10 million per episode to make. Since supply shifts to the left, there is a new equilibrium price and quantity. The market price would increase due to the greater costs of production.
Another reason that could have caused the price of streaming television content to increase could have been an increase in demand. Demand is the number of tv services that people are willing and able to buy at each price. Trends can cause demand to shift. During 2021 and 2022, the UK was recovering or protecting themselves from covid. Therefore, there was a lot of self-isolation. This meant that people to change their hobbies and rely on tv for entertainment. Extract A Line 3 mentioned that 'The demand for individual firms streamed television content boomed when people were forced to stay at home'. This meant that there was a greater quantity demanded at each price, hence a right shift. The diagram below shows the increase in price from p1 to p2 as a result of both a decrease in supply and an increase in demand.
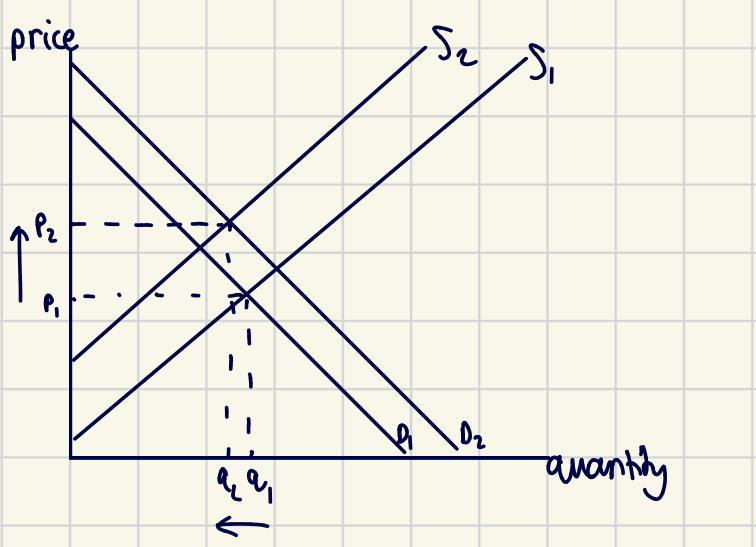
However, there could be other factors which cause the price of tv content to fall instead. For example, there has been an increase in the number of firms in the market. Figure 2 shows ten different firms with at least a 1% market share. If there is an increase in the number of firms in the market, supply would shift to the right because now firms in the market are able to produce more goods and services at each price. Also, as there are multiple factors affecting demand and supply, it is difficult to tell what the main factor is that caused the price to increase.