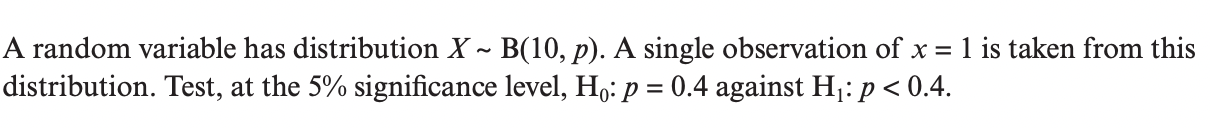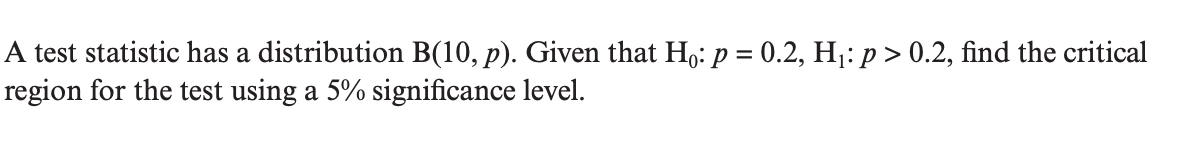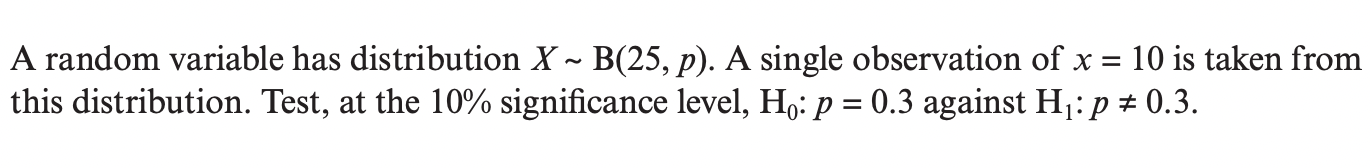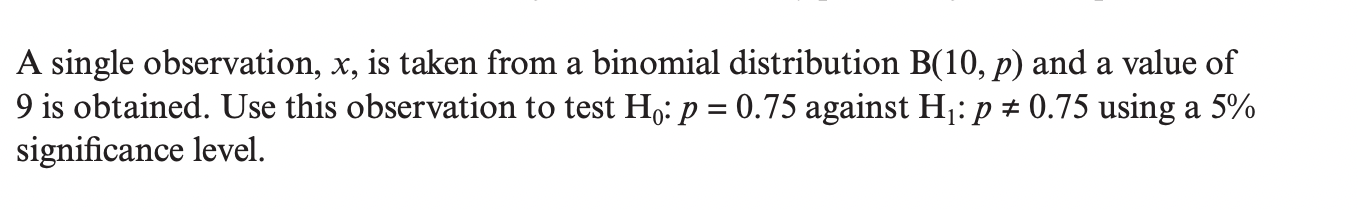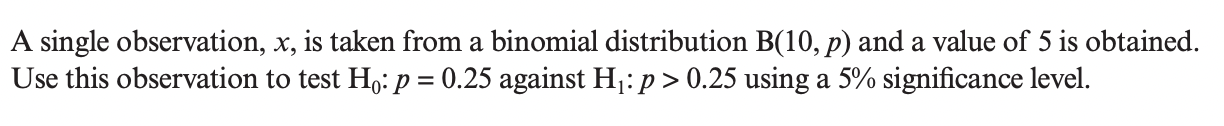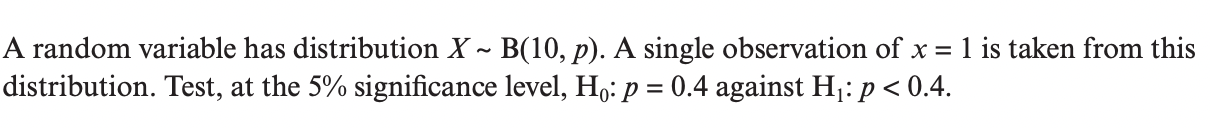A-Level Maths | Binomial Distribution
Last updated on
- Binomial distribution is used to model something where there are two possible outcomes e.g. rain vs not rain, late vs not late.
- X~B(n, p)
- X is a random variable that is binomially distributed with n number of trials and probability of success p
- P(X=x) = (nCr) x (p of success)no. of successes x (p of fails)no. of fails)
non cg50 students
Question 1

Question 2

Binomial distribution practice questions
Question 3

Question 4

Question 5

Question 6

- Hypothesis testing is used to check whether a hypothesis is reliable or not
- state what p represents
- work out relevant probabilities
- If p < 0.05 then there is sufficient evidence to reject our null hypothesis
- If P(X...) > 0.05 then there is insufficient evidence to reject our null hypothesis
Finding critical values
- any values which would lead to a probability less than the significance level which would lead to the null hypothesis being rejected
Question 7
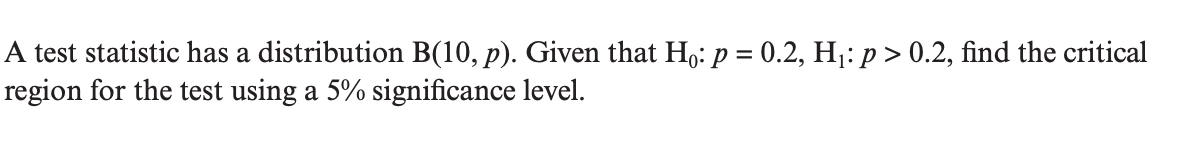
Question 8

Finding critical values in two tails
- For two-tailed tests, half the significance level
Question 9
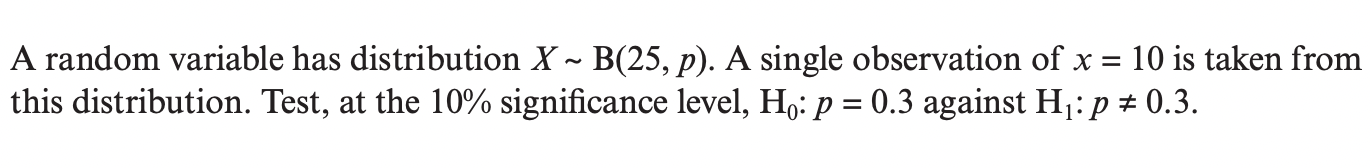
Question 10
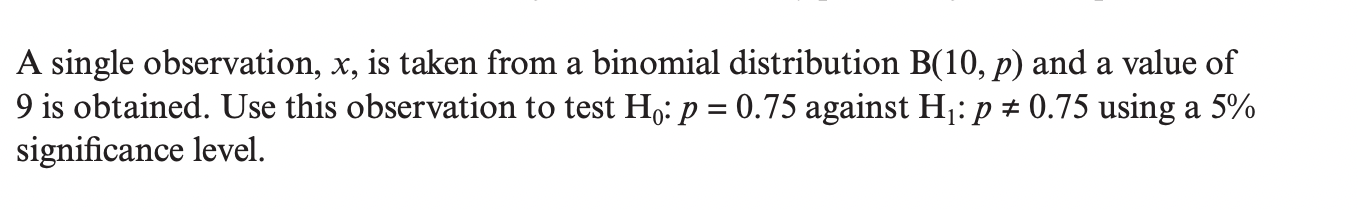
Question 11

Hypothesis testing with one tail
Question 12

Question 13

Question 14
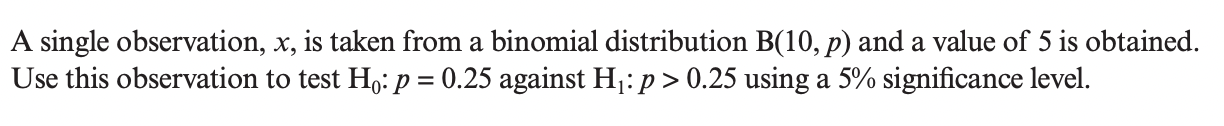
Question 15