Macroeconomic Objectives | A-Level Economics
The four main macroeconomic objectives
- economic growth
- 2% inflation
- low unemployment
- balance of payments on the current account
What is inflation?
When there is an increase in the average price level.
What is deflation?
When there in a decrease in average price level.
What is disinflation?
When the rate of inflation falls but it remains above 0% e.g. from 2% to 1%.
This means that there is still inflation, but it has slowed down.
What are two causes/types of inflation?
Inflation when there is too much demand chasing too few goods and services.
- Demand pull inflation is when the price level increases because of a right shift in aggregate demand.
- Cost push inflation is when the price level increases because of a left shift in short-run aggregate supply.
How is inflation measured?
Inflation is measured by the CPI (consumer price index).
CPI tracks the prices of an average basket of 700 goods/services. Each item has its own weighting.
Retail Price Index (RPI) is an older measure of inflation in the UK that includes housing costs.
What is economic growth?
There are two types of economic growth.
Short-run (actual) economic growth is when there is an increase in real GDP.
Long-run (potential) economic growth is when there is an increase in the productive potential of the economy.
What is real gdp?
- the total value of goods and services produced in the UK economy
What are the stages of the economic cycle?
- boom - high economic growth, low unemployment, high inflation
- downturn
- recession - 2 or more consecutive quarters of negative economic growth
- recovery
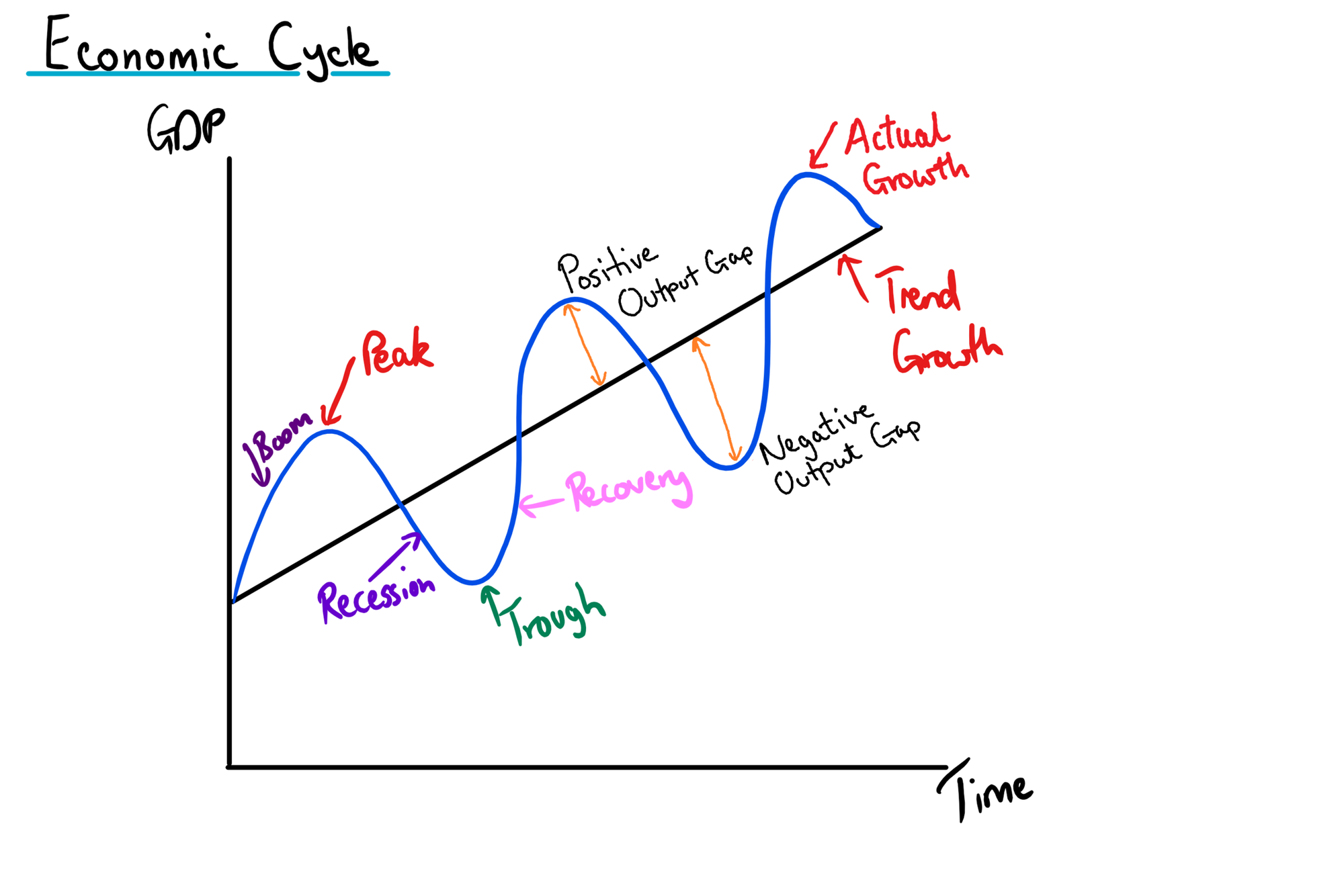
What is a positive output gap?
When actual growth is higher than potential growth
High economic growth and low unemployment, but high inflation.
Use contractionary demand-side policies or supply-side policies.
What is a negative output gap?
When actual growth is lower than potential growth
High unemployment, slow economic growth, and stable prices or even deflation.
Use expansionary demand-side policies.
What are the causes/types of unemployment?
- cyclical
- structural
- frictional
- seasonal
What is cyclical unemployment?
Cyclical unemployment is when there is a lack of aggregate demand in the economy. On average, it affects everyone.
For example, during COVID workers in multiple industries were made redundant as people were asked to isolate at home. Labour is a form of derived demand, so firms would layoff workers.
Implement a policy that causes aggregate demand to increase.
What is structural unemployment?
Structural unemployment happens when there is lack of demand for one specific industry, so workers in that particular industry lose their jobs. They may not have transferable skills to gain a different job.
For example, UK steel industry (it was cheaper to import steel) or black cab drivers.
Implement a policy to re-train workers.